This site is supported by our readers. We may earn a commission, at no cost to you, if you purchase through links.
 You likely do not know that keloids develop in up to 10% of all people after an ear piercing is done. Knowing the difference between a keloid and a piercing bump distinguishes treatment.
You likely do not know that keloids develop in up to 10% of all people after an ear piercing is done. Knowing the difference between a keloid and a piercing bump distinguishes treatment.
In this article, you will learn about the symptoms, causes, and growth patterns that set keloids apart from piercing bumps. We will further discuss some treatment options available and preventive measures, therefore equipping you with information to enable you to confidently manage such conditions.
Read on for specialist insight into managing keloid versus piercing bump distinction
Table Of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- What is a Piercing Bump?
- What is a Keloid?
- Differences Between Piercing Bumps and Keloids
- Other Skin Conditions After Piercing
- Diagnosing Piercing Bumps and Keloids
- Treating Piercing Bumps
- Treating Keloids
- Preventing Keloids
- When to See a Doctor
- The Takeaway
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- How to tell if it’s a keloid or piercing bump?
- Will a keloid on a piercing go away?
- How to get rid of a bump on a piercing?
- Are keloids hard or soft?
- What are piercing bumps & keloids?
- What do keloids look like?
- Can a piercing cause keloids?
- Are hypertrophic piercing bumps and keloid scars the same?
- Can piercing bumps lead to keloids?
- Are keloids more common in certain ethnicities?
- How do lifestyle habits influence keloid development?
- What role does diet play in healing keloids?
- Can existing keloids affect new piercings?
- Conclusion
Key Takeaways
- Keloids aren’t like pesky house guests that leave when you want them to. They’re stubborn overgrowths that can stick around indefinitely.
- Piercing bumps are like temporary roadblocks on your healing journey. They’ll usually disappear with a little TLC, but keloids are more like detours that can take you off course for good.
- If you’re keloid-prone, piercing yourself is like playing Russian roulette. You might get lucky and avoid the bullet, but the odds aren’t in your favor.
- Don’t let keloids get the best of you! There are treatments available to flatten them, shrink them, or even make them disappear. Remember, knowledge is power, and the more you know about keloids, the better equipped you’ll be to keep them at bay
What is a Piercing Bump?
You might notice a small bump forming near your new piercing, which is often a normal part of the healing process. This piercing bump is usually caused by your body’s immune response to the injury, resulting in the formation of extra tissue around the piercing site
Symptoms of a Piercing Bump
You’ve just gotten a new piercing, and now you’re noticing something unusual. Is it a piercing bump? These pesky little bumps are your body’s way of saying, "Hey, what’s going on here?"
You might spot a symmetrical, raised area around your piercing that’s red or pink. Don’t panic if it itches or feels a bit tender – that’s par for the course. You might also notice some crusty bits or a thin, whitish fluid oozing out.
Unlike their cousins, keloids, piercing bumps tend to flatten and lighten over time. Keep an eye on your skin, but remember, these bumps are often just part of the healing process
Causes of a Piercing Bump
You might wonder why you’ve got a bump after getting pierced. Well, it’s your body’s way of saying, "Hey, I’m healing here!" Piercing bumps are caused by your immune system’s response to injury. When you get pierced, it’s like opening a door for bacteria, and your body rushes to close it.
The size and placement of your piercing can affect how your body reacts. Using the wrong jewelry or neglecting proper aftercare can also lead to these pesky bumps. Sometimes, an infection might be the culprit
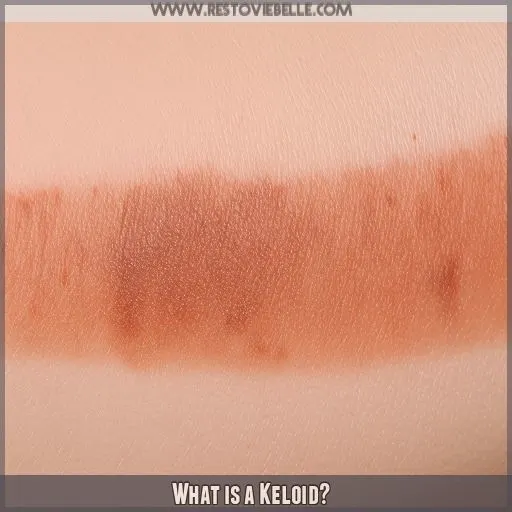
What is a Keloid?
A keloid is a raised scar that grows beyond the boundaries of the original injury, often appearing as a thick, pink or flesh-colored area on your skin. You’re more likely to develop keloids if you’re under 30 or have darker skin tones, and they can be caused by various types of skin trauma, including piercings, surgeries, or even minor injuries
Symptoms of a Keloid
While piercing bumps are temporary, keloids are a more serious matter. These raised scars can be quite troublesome, with symptoms that may include:
- Persistent growth beyond the original injury site
- Discoloration ranging from pink to dark brown
- A smooth, rounded appearance that’s firm to the touch
- Itching, tenderness, or pain in the affected area
Keloids can develop anywhere on your body, but they’re common after piercings. If you’re keloid-prone, you’ll want to be cautious about getting new piercings. Unlike piercing bumps, keloids often require professional treatment. Home remedies might provide some relief, but they won’t make the keloid disappear. Understanding these symptoms helps you differentiate between keloids and typical piercing bumps
Causes of a Keloid
Keloids can form when your body’s healing process goes into overdrive. You’re more likely to develop them if you’ve got a genetic predisposition or darker skin tone. They typically appear after skin trauma, such as surgical wounds or even minor injuries. Here’s a quick breakdown of keloid causes:
| Factor | Impact | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Age | Higher risk | 10-30 years old |
| Genetics | Strong influence | Family history |
| Skin tone | Increased likelihood | Darker complexions |
| Trauma type | Varies | Piercings, surgery |
| Body location | Prone areas | Chest, shoulders |
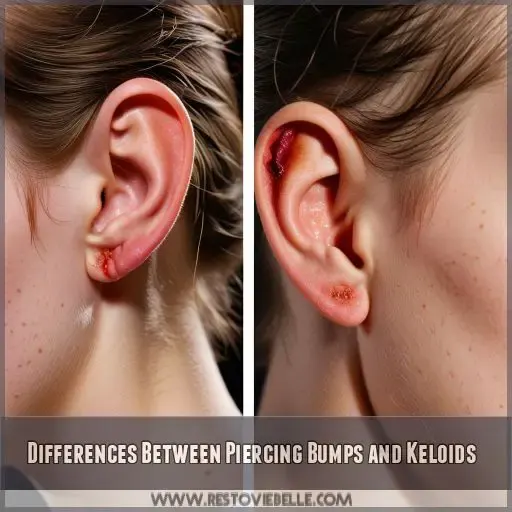
Differences Between Piercing Bumps and Keloids
You’ll notice key differences between piercing bumps and keloids in their appearance, growth patterns, and associated sensations. Piercing bumps typically appear quickly and remain small, while keloids grow slowly over time and can become quite large, with varying colors and textures that may cause itching or pain
Appearance
While one might think that keloids and piercing bumps are identical, there are many noticeable cosmetic differences between these two. You’ll see:
- Piercing bumps are typically small, raised, and symmetrical, often matching your skin tone.
- Keloids, however, are larger, irregularly shaped scars bearing a tumorous nodule appearance.
- Keloids on skin of color are much more prominent, varying from pink to brown.
Recognition of these distinctions is essential to appropriate management of aberrant scar tissue.
Growth Patterns
You’ll notice distinct growth patterns between piercing bumps and keloids. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Characteristic | Piercing Bump | Keloid |
|---|---|---|
| Formation Time | Immediate | Months |
| Size Change | Stable | Grows |
| Location | Near piercing | Can spread |
| Jewelry Impact | May resolve | No effect |
Piercing bumps result from your body’s overproduction of healing tissue, while Keloid scars are hypertrophic scars that continue growing. Understanding these differences can help you identify and address your specific concern
Itching and Pain
You’ll notice differences in itching and pain between piercing bumps and keloids. Piercing bumps often cause mild discomfort, while keloids can be more painful. Here’s what you might experience:
- Piercing bumps: Slight itching, occasional tenderness
- Keloids: Intense itching, persistent pain
- Granulation tissue: Minimal discomfort, may feel sensitive
- Treatment impact: Pain management varies based on the condition
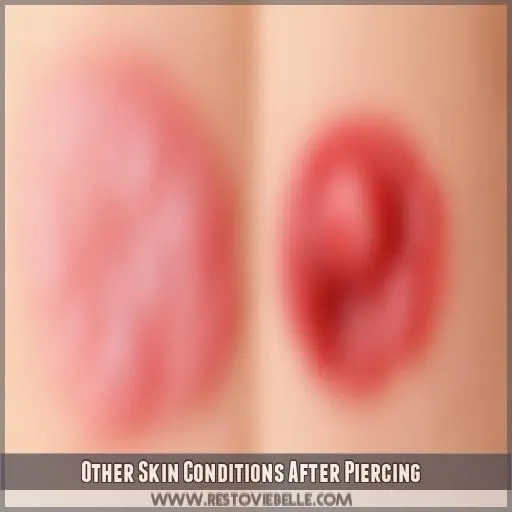
Other Skin Conditions After Piercing
While piercing bumps and keloids are common skin issues after piercings, you should also be aware of other potential complications. Infections can occur, causing soreness, swelling, and yellow pus, while contact dermatitis might lead to blisters, hives, or a burning sensation due to allergic reactions to metals or cleaning products
Infection
While bumps or keloids at the piercing site are a matter of concern, infections become more urgent in terms of danger. You’ll have some redness, swelling, and yellow pus around your piercing site. These symptoms suggest that there’s at least local inflammation and probably some bacterial invasion.
Common causes include poor hygiene or touching the area with dirty hands. Diagnosis of infection requires a physical examination. Your doctor will examine changes on your skin; they may sometimes take cultures.
Treatment will usually involve antibiotics and good cleaning. Follow instructions religiously to minimize the risk of infection during aftercare.
Keep in mind that early detection and treatment can prevent serious complications and save your skin
Contact Dermatitis
Aside from infections resulting in skin complications after piercings, contact dermatitis is also a threat. This is usually the result of contact allergies, which are normally connected with the materials applied in jewelry, notably nickel. You can notice rashes on your skin due to the way that your body’s immune system reacts to them. These symptoms manifest in:
- Blisters
- Hives:
- Itching
- Burning sensation
- Redness
This will be managed by having hypoallergenic jewelry and topical gels applied. Ensure good aftercare for your piercing. You may need to consult a dermatologist for various treatment options available. Avoiding Nickel using stainless steel or titanium if you’re sensitive will prevent such reactions.
Diagnosing Piercing Bumps and Keloids
Diagnosing piercing bumps and keloids starts with a physical exam and a review of your medical history. Doctors assess the appearance, healing time, and scarring potential.
Piercing bumps show up quickly due to the body’s overproduction of healing tissue and usually resolve over time. Keloids, often found as earlobe keloid scars, take months to develop, growing beyond the injury site with fibrous tissue. Rarely, a biopsy might be needed.
Preventive measures and personalized treatment options are guided by these diagnoses
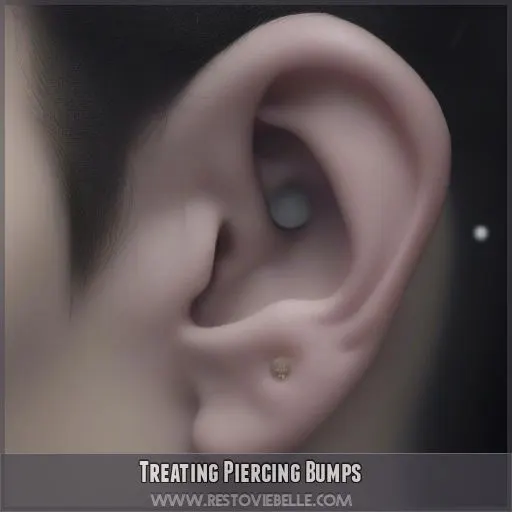
Treating Piercing Bumps
To treat piercing bumps, you might consider methods such as radiation, laser therapy, corticosteroids, topical treatments, or surgery. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best approach for your specific situation
Radiation
Radiation therapy can help treat piercing bumps by reducing the body’s immune response to puncture wounds. Benefits include:
- Less irritation and swelling
- Quick results
- Minimally invasive
- Effective for stubborn bumps
Consult a specialist for advice
Laser Therapy
It involves the application of a particular laser to an affected area in a bid to reduce scar tissue. Some of these lasers include CO2 and pulsed dye, which can create an avenue for this healing process though maintaining a level of laser safety to avoid its side effects like redness or swelling.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are an effective way of treating bumps from a piercing. They reduce swelling and allow the formation of scabs to fall out more quickly by:
- Flattening bumps
• Reduces itching
- Minimizing pain
- Stopping growth
• Prevention of keloids
Regular treatments ensure that the treatment works well with speedy recovery.
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments offer an accessible, cost-effective option for treating piercing bumps. They include both over-the-counter and prescription formulations, aimed at reducing inflammation and promoting healing. Their efficacy varies, but they’re widely available at pharmacies and online
Surgery
If these bumps that are formed as a result of piercing persist, then you may need to undergo surgery. They include removal of the scar and treatments that involve laser therapy.
Corticosteroid injections may be done to decrease inflammation, and radiation may be administered to avoid regrowth.
You should always consult a professional whenever you need advice on how to treat you
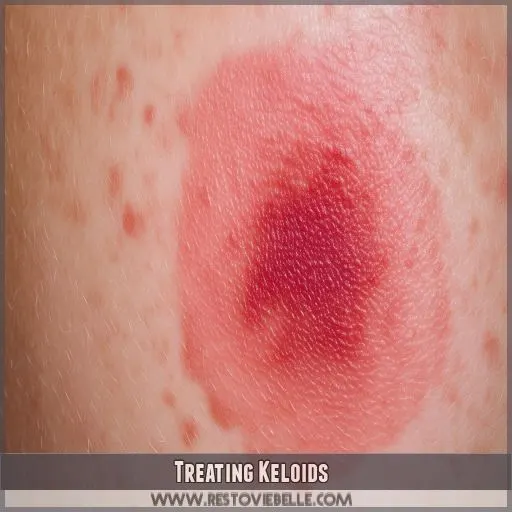
Treating Keloids
Treating keloids involves a few strategies. Cortisone injections can help flatten keloids, while silicone gel or sheets may cover the scar, reducing its appearance.
Laser therapy targets abnormal cell proliferation, potentially shrinking the keloid. For severe cases, debulking surgeries can reduce size, though keloids might reappear.
Radiation therapy is another option to lessen recurrence. Each treatment addresses different aspects of keloid management, aiming to minimize discomfort and improve skin appearance. Always consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best approach
Preventing Keloids
Preventing keloids involves minimizing skin trauma and being mindful of your individual risk factors. If you’re prone to keloids due to genetics, pregnancy, or past experiences, consider these steps:
- Avoid unnecessary piercings or tattoos, especially keloids in ear piercings.
- Use pressure earrings or silicone sheets after any skin injury.
- Consult with a dermatologist for personalized advice and potential use of traditional medicine approaches
When to See a Doctor
If you notice signs of infection, like yellow pus or severe swelling, or if a piercing bump grows larger or changes color, it’s time to see a doctor. Keloids causing significant discomfort or those near your earring need medical attention too. Don’t wait, get professional advice to avoid complications.
| Symptoms | Piercing Bump | Keloid |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Red or pink bump | Raised, irregular scar |
| Growth Pattern | Stays same size | Can grow over time |
| Discomfort Level | Mild itching or pain | Itching, tenderness |
The Takeaway
Knowing how piercing bumps differ from keloids can help you deal with them accordingly. Generally, a bump from a piercing gets smaller in time because it’s just part of your healing and T-cell response, whereas keloids continue growing out from the area of injury due to genetics.
You’ll thus be preventing bumps from forming if you have good skin care and can raise awareness of when you have keloid issues. For persistent issues, consult a doctor to explore the best treatment options tailored to the specific growth patterns and severity of your condition
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How to tell if it’s a keloid or piercing bump?
You can tell it’s a keloid if the scar keeps growing beyond the initial injury, feels thick, and changes color. A piercing bump appears quickly, stays the same size, and typically disappears with proper care
Will a keloid on a piercing go away?
No, a keloid won’t go away on its own. Treatment options include corticosteroids, laser therapy, surgery, or other medical interventions, and without treatment, keloids can continue growing or become more pronounced
How to get rid of a bump on a piercing?
Ironically, the best way to get rid of a bump on a piercing often involves simplicity: use saline soaks, avoid unnecessary irritation, and don’t overdo cleaning products. Sometimes, less really is more
Are keloids hard or soft?
Keloids can be either hard or soft. They often start small and firm but can become softer over time. Their texture varies, and they can feel rubbery. Unlike piercing bumps, they tend to grow beyond the injury area
What are piercing bumps & keloids?
Think of piercing bumps as temporary hiccups in healing, while keloids are stubborn overgrowths. Piercing bumps appear quickly, are small, and don’t grow. Keloids form slowly, expand over time, and can be quite large
What do keloids look like?
Keloids are thick, raised scars that extend beyond the original injury. They can be pink, red, purple, or brown and often grow over time. These scars can be soft or hard and may cause itching or tenderness
Can a piercing cause keloids?
Yes, a piercing can cause keloids, especially if you’re prone to developing them. Keloids form due to an overgrowth of scar tissue, resulting from your body’s excessive healing response to the piercing wound
Are hypertrophic piercing bumps and keloid scars the same?
No, hypertrophic piercing bumps and keloid scars aren’t the same. Hypertrophic bumps stay near the piercing and don’t grow much, while keloids can expand beyond the injury site and get much larger over time
Can piercing bumps lead to keloids?
Most piercing bumps don’t result in keloids themselves; however, if you’re prone to keloid formation, they can. Early recognition and proper care of your piercings will help to avoid possible overgrowth of scar tissue. Always be vigilant!
Are keloids more common in certain ethnicities?
Yes, keloids are more common in individuals with darker skin tones, particularly among African Americans, Asians, and Hispanics. They also tend to occur more frequently in people between the ages of 10 and 30
How do lifestyle habits influence keloid development?
Your lifestyle can impact keloid development. Avoid skin trauma, such as piercings or tattoos, if you’re prone to keloids. Good skin care, like using sunscreen, reduces the risk, but can’t completely prevent them
What role does diet play in healing keloids?
Your diet impacts keloid healing. Consuming foods rich in vitamins C and E, alongside zinc and antioxidants, can support tissue repair and reduce inflammation. Avoid processed foods and sugar, as they can hinder healing
Can existing keloids affect new piercings?
Interestingly, keloids from previous injuries don’t directly impact new piercings, but if you’re prone to keloid formation, you risk developing keloids with new piercings as well. It’s important to consider this risk before proceeding
Conclusion
Knowing the difference between a keloid and a piercing bump is paramount to proper treatment. Their symptoms, causes, and growth patterns place one in a better position to make decisions.
While therapy for piercing bumps might be pretty basic in most cases and revolves around topical treatments or corticosteroids, keloids could be severe and require surgery or laser therapy.
With strategies to prevent them and knowing when to visit your doctor, you can be confidently prepared to deal with these conditions on your own