This site is supported by our readers. We may earn a commission, at no cost to you, if you purchase through links.

Eczema tends to affect larger joints, whereas athlete’s foot is typically localized to the toes.
This article will help you tell them apart and offer guidance on prevention and management.
Table Of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- Is It Athlete’s Foot or Eczema?
- Recognizing Symptoms of Athlete’s Foot and Eczema
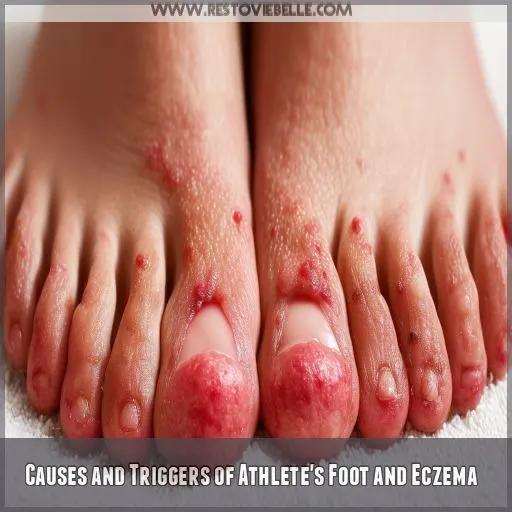
- Causes and Triggers of Athlete’s Foot and Eczema
- Diagnosis Methods for Athlete’s Foot and Eczema
- Treatment Approaches for Athlete’s Foot and Eczema
- Living With Athlete’s Foot or Eczema
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- How do I know if it’s athlete’s foot or eczema?
- How do I know if it’s eczema or fungus?
- How can you tell the difference between tinea and eczema?
- Will eczema cream help athlete’s foot?
- How common are these skin conditions?
- Are there natural remedies for these?
- Can I catch either from my partner?
- Can these conditions be cured?
- What are the long-term effects?
- Conclusion
Key Takeaways
If your feet are itchy, don’t jump to conclusions! Athlete’s foot and eczema may look similar, but they are different conditions. Athlete’s foot tends to appear between your toes, whereas eczema can show up anywhere. To distinguish between the two, look for red, peeling skin, indicative of athlete’s foot, and red, inflamed skin, which suggests eczema. Treat them accordingly: fight athlete’s foot with antifungal medication and tackle eczema with Topical steroids.
Is It Athlete’s Foot or Eczema?
Distinguishing between athlete’s foot and eczema can be challenging due to their similar presentations.
Athlete’s foot, a fungal infection, typically occurs between the toes, causing intense itching, scaling, and blistering.
Eczema, on the other hand, is a general term for various skin conditions characterized by inflammation. It can appear anywhere on the body, presenting as itchy, red, and dry patches.
To differentiate, look for distinct patterns: athlete’s foot favors the toe web spaces, while eczema often presents in a more scattered distribution.
Recognizing Symptoms of Athlete’s Foot and Eczema
To distinguish between athlete’s foot and eczema, closely examine the skin’s appearance and associated symptoms. Athlete’s foot typically shows red, peeling skin between the toes, while eczema often presents with red, itchy patches that can appear anywhere on the body.
Differentiating Between Skin Appearance
Regarding differentiating skin appearance for athlete’s foot and eczema, several key distinctions exist. Athlete’s foot commonly manifests as peeling, cracked skin and blisters, usually between the toes or on the feet. Conversely, eczema can cause red, inflamed skin and blisters, but it can manifest anywhere on the body, particularly around the knees and elbows.
While both conditions can result in itchy, irritated skin, the rash’s texture and location can provide clues as to which condition may be present. Athlete’s foot typically thrives in damp environments, so increased itching and irritation may be noticed in those areas. Eczema, however, tends to be triggered by various factors, such as allergens or stress, and can flare up anywhere.
Identifying Common Symptoms
Athlete’s foot and eczema are common skin conditions with similar symptoms, including itching and redness. Here’s how to identify and manage them:
- Recognize the symptoms: Athlete’s foot often causes itching, peeling, and blisters between the toes or on the feet. Eczema, on the other hand, typically presents with itchy, red, inflamed skin anywhere on the body, but especially around the knees and elbows.
- Prevent flare-ups: Keep your skin healthy and avoid triggers. For athlete’s foot, this means practicing good foot hygiene and avoiding damp environments. For eczema, identify and avoid triggers like allergens and irritants, and keep your skin moisturized.
- Manage symptoms: If you experience symptoms, seek treatment. For athlete’s foot, this may include antifungal medications and foot hygiene. For eczema, treatment options range from topical steroids to light therapy and oral medications.
Itchy feet? Redness and blisters? Don’t scratch that itch just yet—it could be athlete’s foot or eczema. Learn the differences and get the right treatment.
Causes and Triggers of Athlete’s Foot and Eczema
Athlete’s foot is caused by a contagious fungal infection, and thrives in warm, moist environments like gyms and pools. Eczema, often influenced by genetic factors, can be triggered by environmental elements such as allergens, irritants, and stress.
Understanding Fungal Infection and Genetic Factors
Understanding the causes and triggers of Athlete’s Foot and Eczema depends on recognizing the impact of fungal infections and genetic factors.
Athlete’s Foot is primarily caused by a fungal infection, specifically by dermatophytes, which thrive in humid, shared environments, leading to contagious infections.
On the other hand, Eczema is influenced by a combination of genetic predispositions and environmental triggers.
While genetics can make individuals more susceptible to Eczema, environmental factors, such as allergens and irritants, often initiate or aggravate the condition, causing flare-ups.
Environmental Triggers for Eczema
Now that you comprehend the role of fungal infections and genetic factors in causing athlete’s foot and eczema, let’s delve into the environmental triggers specific to eczema.
Eczema can be triggered by various environmental factors, including allergens, irritants, temperature changes, and stress. These triggers can initiate or exacerbate eczema symptoms, so identifying and managing them is imperative. Allergens like pollen and pet dander, irritants such as harsh chemicals or soaps, and temperature fluctuations can all spark an eczema flare-up. Stress, while not an environmental factor in the traditional sense, also plays a significant role in triggering eczema symptoms. Effective management of eczema involves recognizing and limiting exposure to these triggers, which can assist in keeping your skin condition under control.
Diagnosis Methods for Athlete’s Foot and Eczema
To diagnose athlete’s foot or eczema, your doctor will first take a thorough medical history to understand your symptoms and potential triggers. They may also perform a physical examination and potentially order a skin test to confirm the underlying condition.
Medical History Importance
Knowing your medical history is critical for the early diagnosis and effective treatment of conditions like athlete’s foot and eczema.
A thorough assessment involves understanding your health, lifestyle, and previous experiences.
This helps doctors identify the root cause and tailor treatment plans to your specific needs.
Patient involvement is key, so be sure to communicate openly with your doctor about any concerns, symptoms, or past health issues you may have.
Physical Examination and Skin Test Differences
Several methods help distinguish between athlete’s foot and eczema through physical examinations and skin tests.
Skin scraping comparison involves examining skin cells under a microscope for signs of fungal or bacterial infection.
Culture testing involves cultivating samples in a laboratory to confirm the presence of pathogens.
The KOH test dissolves skin cells to better visualize any fungal elements present.
Wood’s lamp examination uses ultraviolet light to detect specific bacteria or fungi.
These diagnostic tests are useful in differentiating between athlete’s foot, which can present with red, pus-filled bumps, and eczema.
Treatment Approaches for Athlete’s Foot and Eczema
When treating athlete’s foot, antifungal medications are key, whereas eczema often requires topical steroids. Incorporating lifestyle adjustments and prevention strategies can help manage both conditions effectively.
Antifungal Medications Versus Topical Steroids
When discussing treatment, athlete’s foot and eczema demand distinct approaches. For athlete’s foot, a fungal infection, antifungal medications are the preferred treatment choice. These are available as topical creams or ointments, or oral medications.
In contrast, eczema is typically managed with topical steroids, which aid in reducing inflammation and itching. It’s crucial to recognize that:
- Topical steroids vary in strength and formulation, and their use should be guided by a healthcare professional to guarantee safe and effective application.
- The treatment objective for eczema is to manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups, as there’s currently no cure.
- Long-term management of eczema may also include additional medications, such as topical antihistamines and emollient creams, to provide relief and maintain skin health.
Lifestyle Adjustments and Prevention Strategies
Once you’ve determined whether you’re dealing with athlete’s foot or eczema and have selected the appropriate treatment, it’s essential to make lifestyle adjustments and adopt prevention strategies to keep these conditions at bay.
For athlete’s foot, good foot hygiene** is essential. Wash your feet daily with soap and be sure to dry them thoroughly, especially between your toes. Alternate your shoes daily, and always opt for breathable footwear to keep your feet dry. Avoid walking barefoot in public areas like pools or gyms, as these are breeding grounds for the fungus that causes athlete’s foot.
If you have eczema, it’s imperative to identify and avoid triggers. Common irritants include pollen, pet dander, harsh chemicals, and scented products. Moisturizing regularly with hypoallergenic products can help prevent dry skin and reduce flares. Managing stress and maintaining a healthy diet are also beneficial strategies for keeping eczema under control.
Living With Athlete’s Foot or Eczema
Managing daily life with athlete’s foot or eczema requires consistent adherence to your treatment regimen for effective control. You must follow prescribed treatments and maintain good hygiene practices to prevent flare-ups and complications.
Daily Management Tactics
In terms of daily management, consistency is paramount. Adhere to a routine that incorporates regular skin care and lifestyle modifications. Select footwear that offers protection, opt for products that don’t cause allergies, and maintain a routine that’s gentle on the skin to alleviate symptoms. Ensure your skin remains healthy and radiant!
Importance of Adherence to Prescribed Treatments
Adhering to prescribed treatments is essential for managing athlete’s foot or eczema and preventing flare-ups.
Medication adherence, or patient compliance, is key to treatment effectiveness.
It’s important to follow your doctor’s instructions and take medications as directed. Don’t skip doses or stop treatment early, even if symptoms improve.
Attend follow-up appointments to monitor progress and make any necessary adjustments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How do I know if it’s athlete’s foot or eczema?
To determine whether you have athlete’s foot or eczema, consider the location and symptoms. Athlete’s foot usually affects the feet, especially between the toes, causing itching, peeling skin, and blisters. Eczema can develop anywhere but is common around the knees and elbows, with symptoms like itchiness, red skin, and a rash.
How do I know if it’s eczema or fungus?
Eczema and fungal infections can look similar, but they’ve different causes and treatments. See a healthcare professional if you’re unsure. Fungal infections usually present with a red, scaly, and itchy rash with occasional pustules.
How can you tell the difference between tinea and eczema?
Tinea is a fungal infection that causes itchy, red patches with hair loss between them. It’s usually round with a defined edge and has small black dots in the center. Eczema causes dry, scaly patches and is often genetic.
Will eczema cream help athlete’s foot?
No, eczema cream won’t treat athlete’s foot. Athlete’s foot is a fungal infection, so you’ll need an antifungal medication.
How common are these skin conditions?
As the adage goes, knowledge is power. So, let’s empower you with some insights into the prevalence of these skin conditions. Eczema and athlete’s foot are common, affecting millions worldwide. Over 31 million people in the US alone have some form of eczema. Athlete’s foot is often caught in communal areas, like gym showers.
Are there natural remedies for these?
For athlete’s foot, consider trying tea tree oil. It has antifungal properties that may help alleviate symptoms naturally. As for eczema, some find relief with colloidal oatmeal baths or coconut oil due to their anti-inflammatory effects. However, always consult a healthcare provider before starting any new treatment regimen.
Can I catch either from my partner?
Eczema isn’t contagious, so you won’t catch it from your partner. Athlete’s foot, however, is highly contagious and can spread through skin-to-skin contact or contact with contaminated surfaces, such as towels and shoes.
Can these conditions be cured?
Eczema is a chronic condition without a cure, but it can be treated and managed with medication and lifestyle changes. Athlete’s foot can be treated with over-the-counter or prescription antifungal medication, but it may keep coming back.
What are the long-term effects?
If left untreated, the fungal infection of athlete’s foot can spread to other parts of the body. Eczema, on the other hand, is a chronic condition that requires long-term management to prevent flare-ups.
Conclusion
Distinguishing between athlete’s foot and eczema can be challenging.
However, with the knowledge gained from this article, you can confidently identify and manage these conditions.
[Keypoints]You now have the tools to:
- Differentiate between the two conditions based on their symptoms and causes.
- Understand how to get an accurate diagnosis.
- Explore effective treatments to manage them.
The next time you or someone you know encounters the "itchy feet" conundrum, you’ll be prepared to address it and provide relief.