This site is supported by our readers. We may earn a commission, at no cost to you, if you purchase through links.
Oily skin can present unique aging characteristics compared to dry skin, which is largely a result of sebum’s protective nature. Understanding sebum’s role, how collagen degrades, and environmental influences are key factors.
Let’s explore the unexpected truth about skin aging and its relationship with skin type.
Table Of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Oily skin may not be a magical fountain of youth, but it sure knows how to keep the wrinkles guessing with its unique aging journey.
- Sebum, the natural oil production star, plays a crucial role in oily skin’s aging process by being both a protective shield and a hydration hero.
- While oily skin can dodge some fine lines thanks to its oiliness, it’s not immune to developing deeper wrinkles, especially in the lower face.
- Embracing the individuality of all skin types in the aging marathon shows that oily skin, while having its perks, doesn’t sprint past the finish line without facing its own aging challenges.
Does Oily Skin Age Better?
Contrary to common belief, oily skin doesn’t necessarily age better than dry skin; it simply ages differently. Oily skin often has larger pores and a thicker dermis, which can result in unique wrinkle patterns and a smoother appearance.
The sebum produced acts as a natural moisturizer and protective barrier, but excess production can lead to acne and complicate skincare. Factors like cellular metabolism, genetic background, and sun exposure affect aging regardless of skin type. While oily skin might seem to age more gracefully, understanding and managing your skin type is key.
Curious about maintaining a youthful glow? Here’s the scoop!
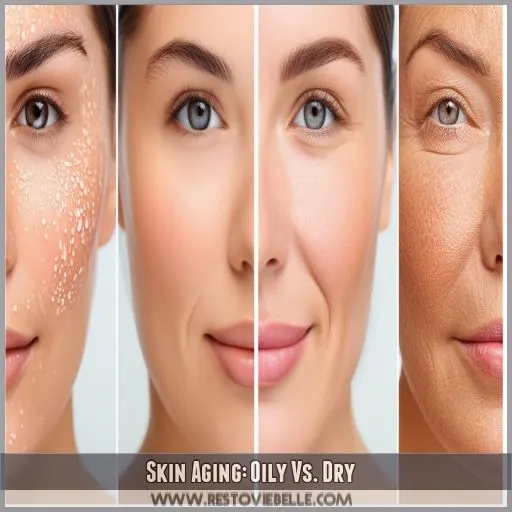
Skin Aging: Oily Vs. Dry
You’ve probably heard that oily skin ages better than dry skin, but is it true? Let’s explore the details of skin aging.
Oily skin tends to have larger pores and a thicker dermis, which can lead to different wrinkle patterns compared to dry skin. While dry skin might show fine lines earlier, oily skin isn’t off the hook. It’s all about elasticity differences and hydration levels.
Surprisingly, oily skin can be prone to scarring, which might affect its aging appearance.
Understanding your skin type is key to managing the aging process and keeping your complexion in tip-top shape.
The Role of Sebum in Oily Skin
Sebum, the natural oil your skin produces, plays an important role in oily skin’s health and appearance. It’s composed of lipids that help maintain your skin barrier, keeping it moisturized and protected.
Your sebaceous glands regulate sebum production, influenced by hormones like testosterone. While excess sebum can lead to acne, it also interacts with skincare products, potentially affecting their efficacy.
Notably, sebum has a complex relationship with your skin’s microbiome, supporting beneficial bacteria.
Understanding sebum’s function is essential to managing oily skin effectively and harnessing its potential benefits for skin health.
Factors Influencing Aging in Different Skin Types
While sebum production plays a role in how your skin ages, it’s not the only factor at play. Collagen breakdown and environmental influences also substantially impact the aging process, affecting both oily and dry skin types in unique ways.
Sebum Production Impact
Your skin’s sebum production plays a vital role in its aging process. While oily skin might seem like a nuisance, it can actually be a blessing in disguise for aging. Here’s how sebum impacts your skin’s aging process:
- Sebum acts as a natural moisturizer, keeping your skin hydrated and plump
- It forms a protective barrier against environmental stressors, potentially slowing down aging
- The lipid balance in sebum influences your skin’s microbiome, which can affect overall skin health
Collagen Breakdown Variations
While sebum production plays a role, collagen breakdown is another key factor in skin aging. Your skin type influences how this process unfolds. Let’s explore the variations:
| Factor | Oily Skin | Dry Skin |
|---|---|---|
| Cellular metabolism | Faster | Slower |
| Enzymatic activity | Higher | Lower |
| Genetic predisposition | Variable | Variable |
| Hormonal influences | Stronger | Weaker |
| Structural differences | Thicker dermis | Thinner dermis |
Skin experts note that these differences can affect how fine lines develop. However, sun exposure and free radicals remain universal threats, making UV protection essential for all skin types.
Environmental Factor Effects
Environmental factors such as UV exposure from the sun can cause oxidative stress, DNA damage, and protein and lipid impairment
Misconceptions About Oily Skin Aging
There are a few misconceptions about oily skin and aging that need to be addressed.
| Myth | Reality |
|---|---|
| Oily skin doesn’t wrinkle. | Oily skin ages differently, developing different types of wrinkles. |
| Oily skin means more hydrated skin, so fewer wrinkles. | A study found that skin oiliness doesn’t impact the development of crow’s feet. |
| Oily skin ages more slowly. | Oily skin ages at a similar rate to other skin types but may appear smoother due to sebum production. |
While it’s true that oily skin may exhibit some types of wrinkles less prominently, it doesn’t mean it’s immune to the aging process. Oily skin can still develop deeper lines in the lower face due to loss of tone.
The key takeaway is that all skin types age uniquely, and generalizations about superior aging are inaccurate.
Skincare Tips for Aging With Oily Skin
Now that we’ve debunked the myth that oily skin always equals youthful skin, let’s focus on some practical skincare tips to help you age gracefully with your oily skin type. Here are four things to keep in mind:
- Cleanser Choices: Opt for gentle, foaming cleansers with exfoliating ingredients like salicylic acid or beta-hydroxy acid. Avoid harsh, drying cleansers and oil-based or alcohol-based cleansers, as they can irritate the skin and trigger increased oil production.
- Face Care: Incorporate a water-based moisturizer with hyaluronic acid to keep your skin hydrated without adding excess oil. Look for oil-free, non-comedogenic products that won’t clog your pores.
- Sunscreen: Protect your skin from the sun’s harmful rays by using sunscreen daily. Choose lightweight, non-occlusive sunscreens that are labeled "oil-free" and "non-comedogenic." Look for ingredients like zinc oxide, titanium dioxide, and antioxidants to protect and nourish your skin.
- Skincare Habits and Diet: Develop healthy skincare habits such as washing your face regularly, twice daily, and always removing your makeup before bed. Additionally, focus on adopting a healthy diet rich in skin-essential nutrients and getting sufficient sleep to promote overall skin health from within.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Does oily skin always look younger?
Well, it’s not quite that simple. Oily skin may give the illusion of youth with its dewy appearance, but it doesn’t grant you eternal youth.
While oily skin may have its perks, it’s not a ‘golden ticket’ to avoiding wrinkles.
Does oily skin cause wrinkles?
Oily skin doesn’t cause wrinkles, but it can influence their appearance. Oily skin may have less noticeable "crinkly" fine lines on the forehead due to thicker skin and larger pores. However, it can also develop deeper lines in the lower face due to loss of tone.
Does oily skin need moisturiser?
Yes, even oily skin needs moisturizer. While it may seem counterintuitive, moisturizers help regulate oil production and prevent dehydration, which can trigger excess oil and acne. Choose a lightweight, water-based, non-comedogenic moisturizer with ingredients like hyaluronic acid.
Can I prevent premature ageing?
While you can’t stop the natural aging process, you can take steps to prevent premature aging. Protect your skin from the sun, eat healthily, exercise regularly, quit smoking, manage stress, and get quality sleep.
Does diet impact skin ageing?
Yes, diet can impact skin aging.
Nutrition and its reflection on skin has always been an interesting topic for scientists and physicians throughout the centuries worldwide. Vitamins, carotenoids, tocopherols, flavonoids, and a variety of plant extracts have been reported to possess potent anti-oxidant properties and have been widely used in the skin care industry either as topically applied agents or oral supplements in an attempt to prolong youthful skin appearance.
L-ascorbic acid (vitamin C) is water soluble, photosensitive, and is the most important antioxidant in the hydrophilic phase. Vitamin C isn’t naturally synthesized by the human body and therefore adequate dietary intake of vitamin C is required and essential for a healthy human diet.
Vitamin E is a fat-soluble membrane bound antioxidant and consequently a free-radical scavenger especially of highly reactive singlet oxygen. Tocopherol is like vitamin C a naturally occurring endogenous non-enzymatic antioxidant.
Carotenoids are vitamin A derivates like β-carotene, astaxanthin, lycopene and retinol, which are all highly effective antioxidants and have been documented to possess photoprotective properties.
Resveratrol is an antioxidant, natural polyphenol, abundant in the skin of grapes (but not in the flesh). Resveratrol and its oligomeres, trans-piceatannol, the dimers epsilon-viniferin, ampelopsin, iso-epsilon-viniferin, the trimers miyabenol C and the tetramers hopeaphenol, R-viniferin and R2-viniferin belong to the sub-group of stilbenes.
Curcumin is the principal curcuminoid of the popular Indian spice turmeric, which is a member of the ginger family (Zingiberaceae) and is frequently found in rice dishes to add yellow color to the otherwise white rice.
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is a fat-soluble, endogenous (synthesized by the body), vitamin-like substance that’s mainly stored in the fat tissues of our body. It’s present in most eukaryotic cells, primarily in the mitochondria and plays an important role as a component of the electron transport chain in the aerobic cellular respiration, generating energy.
Essential Fatty Acids (EFAs) are long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids derived from linolenic, linoleic and oleic acids. They can’t be produced in the human body and they’ve to be consumed through our daily dietary intake.
Glycation of the skin can lead to a loss of elasticity and wrinkling, sagging skin. Foods that cause a spike in the level of sugar in your blood stream can also cause collagen damage. This is due to a process known as glycation. In this process, elevated levels of sugar can attach to proteins in the skin to form harmful molecules. These molecules are called advanced glycation end products, which researchers call (very fittingly) AGEs. The proteins in the skin that are most impacted are collagen and elastin fibers.
Glycation of the skin can lead to a loss of elasticity and wrinkling, sagging skin. Foods that cause a spike in the level of sugar in your blood stream can also cause collagen damage. This is due to a process known as glycation. In this process, elevated levels of sugar can attach to proteins in the skin to form harmful molecules. These molecules are called advanced glycation end products, which researchers call (very fittingly) AGEs. The proteins in the skin that are most impacted are collagen and elastin fibers.
Conclusion
It’s a common misconception that oily skin ages better than dry skin. While oily skin may develop fewer fine lines due to its natural moisture, it’s not the only factor in skin aging. Dry skin, though more prone to wrinkles, doesn’t always equate to deeper lines or an older appearance.
So, does oily skin age better? The answer is: not exactly.











